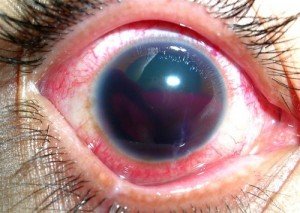
Hyphema refers to an eye injury which results in bleeding within the eye’s anterior chamber. The anterior chamber lies in front of the pupil and is a fluid-filled space beneath the cornea of the eye. 75% of the hyphema cases report normal vision, after the symptoms have been resolved.
Important Disclaimer: this blog on Hyphema is for information purposes only. To learn to recognize and manage minor and severe head and eye injuries enrol in first aid courses with St Mark James.
Causes
Hyphema is caused due to the rupture of the blood vessels in the iris of the eye. Some of the most common causes of eye bleeding or hyphema include:
- Occupational/industrial injuries
- Sports injury
- Altercations and fist fights
Signs and symptoms
Some of the common signs and symptoms of hyphema of the eye include:
- Accumulation of blood in front of the pupil of the eye
- Redness of the eye
- Pain
- Vision changes such as blurred vision or even loss of vision
- Bruises around the eye
When to seek medical attention
See your doctors if any of the symptoms result from hyphema:
- Bleeding that worsens
- Cloudiness of the eye worsens
- The colored region of the eye appears red or is covered with blood
- Dual vision
- Worsening vision
- Eye pain that worsens
- Drainage of pus from the eye
Doctors may prescribe plenty of rest along with narcotic pain medication, aminocaproic acid eye drops, an eye shield, corticosteroid eye drops and other treatment medication that dilate the pupils. Only a few cases of hyphema require surgery.
Complications
Some of the complications that may result from hyphema include:
- Reduced vision
- Cornea may become permanently stained
- Bleeding is recurrent within the anterior chamber of your eye
- Glaucoma
Treatment
After calling 911, follow these treatment steps until help arrives:
- Protect the eye from further injury
- Use a clean cloth to cover the eye
- Make sure you do not apply pressure on your eyeball
- Avoid taking NSAIDs or blood thinners such as ibuprofen or aspirin as they may exacerbate the bleeding
At the hospital
Your doctor will examine your eye and advise treatment depending on the underlying cause of the condition and the severity of the bleeding. Doctors may additionally, prescribe eye drops and recommend wearing an eye patch till the eye recovers. Surgery is rarely required to treat hyphema.
Home care tips
Experts recommend the following home care tips to treat the symptoms of hyphema:
- Limit your activity as directed by your health care provider
- Raise the head of your bed so that you head is elevated while resting
- DO NOT take aspirin
- DO NOT take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs):
- Ibuprofen
- Ketoprofen
- Naproxen
- Take over-the-counter pain medication such as acetaminophen to relieve pain
- An eye shield can be used as directed by your health care provider
- Take medication prescribed by your health care provider as directed. Avoid skipping doses as it just makes the medicine less effective. It is helpful if you familiarize yourself with the side-effects of the medication prescribed to you by your doctor
Learn More
To learn more about minor and major head and neck injuries enrol in St Mark James first aid courses (register here) via credible providers.
Related Video
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AP4_rmZ6tOo